An F1 race is a spectacle of speed and precision. Let’s dive into the world of F1 trackside positions, a blend of physical prowess, technical expertise, and split-second decision-making that keeps these high-performance machines on the track.
 1. Race Engineer: The Driver’s Strategist
1. Race Engineer: The Driver’s Strategist
In every F1 team, a Race Engineer forms the critical link between the driver and the car. They are tasked with understanding the driver’s feedback and using it to tweak the car’s setup for optimum performance. On race day, the Race Engineer oversees the execution of the race strategy, reacting to on-track events and ensuring the driver is aware of the car’s condition and any tactical changes needed. This role requires a deep understanding of vehicle dynamics and data interpretation, and strong communication skills.
Career Path to Becoming a Race Engineer
Becoming a Race Engineer requires a potent blend of technical know-how, practical experience, and an in-depth understanding of motor racing. Here’s an idea of a simplified roadmap to guide you on your journey:
Basic Qualifications:
A degree in mechanical engineering, automotive engineering, or a related field is usually the stepping stone for a career as a Race Engineer. These programs will equip you with a solid foundation in the principles of vehicle design, dynamics, and systems.
Specialising with a Master’s Degree:
To deepen your knowledge and set yourself apart from the competition, a master’s degree specialising in motorsport engineering or race car design can be incredibly beneficial. You could also benefit from Formula Student competitions.
Gaining Relevant Experience:
Hands-on experience is a key factor in becoming a Race Engineer. Start by seeking internships or work placements with racing teams, even at the lower levels. And again, participating in events like Formula Student provides an excellent platform for gaining practical experience.
Climbing the Ladder:
Start your career with junior roles within a racing team, such as a data analyst or performance engineer, and gradually work your way up. Be ready to spend several years learning and gaining experience within the racing environment.
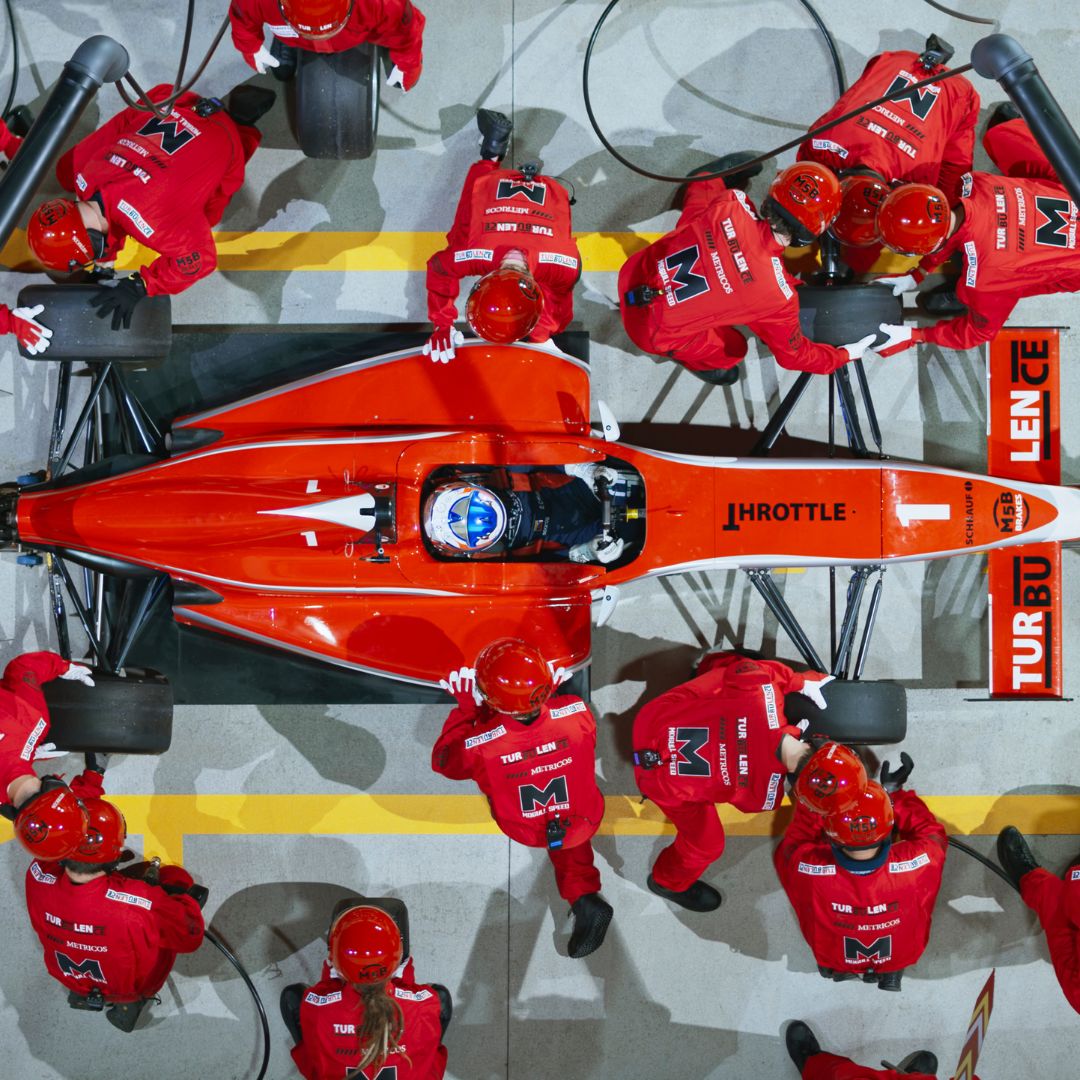 2. Pit Stop Crew: Speed and Synchrony
2. Pit Stop Crew: Speed and Synchrony
The pit stop crew, often composed of over 20 members, are the epitome of speed and coordination. This group includes Tyre Mechanics, who rapidly replace the car’s tyres, the Front and Rear Jack operators responsible for lifting the car, and the Stabilising Crew, tasked with preventing lateral movement. Then, there are the ‘gunners’ who operate the wheel guns to unscrew and tighten wheel nuts. In the heart-stopping seconds of a pit stop, each crew member’s precision and speed can make all the difference.
Career Path to Joining a Pit Stop Crew
Joining a Pit Stop Crew requires a unique combination of technical skills, physical fitness, and mental agility. Here’s a brief guide to help you on this path:
Acquiring Basic Automotive Knowledge:
A fundamental understanding of automotive mechanics is essential. Many members of pit crews have backgrounds as mechanics or engineers, and relevant vocational training or qualifications can be extremely useful. Understanding the intricacies of race cars, including their tyres and wheel mechanisms, is critical.
Physical Training:
Pit crew members need to be physically fit and agile. The high-pressure environment of a pit stop requires quick reflexes, strength, and endurance. Regular fitness training, including strength, cardio, and agility workouts, is a must.
Gaining Experience:
Hands-on experience is invaluable. Begin with involvement in lower-tier motorsport events, such as local or national racing series. This provides an opportunity to learn the ropes, understand race protocols, and build up speed and precision.
Specialist Training:
There are a few training programs specifically designed for aspiring pit crew members, teaching the skills needed to safely and efficiently conduct pit stops. These programs often involve simulated pit stop scenarios to hone your skills under pressure.
Joining a Team:
Once you have the necessary skills and experience, the next step is to join a racing team. This may initially be in a smaller, lower-profile series, but with dedication and proven skill, opportunities with larger, potentially even Formula 1 teams, can follow.
 3. Team Strategist: The Master Planner
3. Team Strategist: The Master Planner
Formulating the right strategy can be the difference between winning and losing in F1. The Team Strategist analyses data related to weather, tyre wear, fuel usage, and rivals’ performance to develop the race plan. During the race, the strategist must adapt to changing circumstances, making critical decisions on pit stop timings, tyre choices, and fuel strategy. This role demands a deep understanding of F1 regulations, analytical prowess, and an ability to make rapid, sound decisions.
Career Path to Becoming a Team Strategist
The journey to becoming a Team Strategist is typically steeped in experience, technical knowledge, and a profound understanding of motorsport dynamics. Here’s an example of some of the steps involved:
Acquiring a Solid Educational Foundation:
Start with a degree in engineering, mathematics, physics, or data science. This gives you the theoretical foundation to understand the mechanics of racing, the ability to analyse complex data, and a grounding in problem-solving techniques.
Gaining Motorsport Knowledge:
Develop a deep understanding of the world of motorsports and, specifically, Formula 1. Understand the rules and regulations, the nuances of different race tracks, and the variables that can impact a race. Following F1 closely and studying past races can provide useful insights. Keep a diary of strategically-interesting races so you can look back on them to study.
Gaining Experience:
Try to get involved with racing at any level, whether it’s karting, junior formulas, or even sim racing. Experience in these environments will help you understand the real-world implications of strategic decisions and how different variables can impact a race.
Master’s Degree or Specialised Courses:
Further education in motorsport engineering or data analysis can provide a more focused understanding of the strategic elements of racing. There are specific courses that delve into race strategy, data analysis, and team management.
Joining a Team:
Start your career with a motorsport team, perhaps in a junior role within the strategy department or in data analysis. This will provide you with invaluable on-the-job training and a chance to learn from experienced strategists. Sometimes there are also junior strategy roles that pop up in F1, like this one: https://formulacareers.com/job/junior-strategy-analyst/ (closing date: June 25th 2023) Always check teams’ careers pages just in case an interesting opportunity arises!
 4. Performance Analysts: The Data Whisperers
4. Performance Analysts: The Data Whisperers
F1 is a sport governed by data. Performance Analysts sift through the myriad of information from sensors on the car and interpret it into actionable advice. They analyse metrics such as tyre performance, aerodynamic data, fuel efficiency, and more. Their insights inform tactical decisions and car setup changes, aiming to shave off those crucial fractions of a second. As such, a background in data analysis and a detailed understanding of F1 car systems are essential for this role.
Career Path to Becoming a Performance Analyst
Becoming a Performance Analyst in F1 is a blend of technical acumen, attention to detail, and a deep passion for motorsport. Here’s a suggested career path:
Pursuing an Appropriate Education:
This journey typically starts with a degree in a field such as data science, physics, mechanical engineering, or computer science. These subjects provide a strong foundation in data analysis and understanding the physics of motor racing.
Gaining Technical Proficiency:
Performance analysts need to be adept at using various data analysis tools and software. Proficiency in programming languages and data visualisation tools, is highly beneficial.
Deepening Motorsport Knowledge:
Develop a deep understanding of the world of motorsports, specifically F1. Familiarise yourself with the systems and components of an F1 car, understand how different factors such as tyre wear, aerodynamics, and fuel efficiency affect performance.
Gaining Experience:
Try to gain experience in data analysis roles, ideally within the automotive or motorsport industry. Internships or entry-level roles can provide practical experience and help you understand how data informs decision-making in this context.
Specialised Training and Education:
Consider postgraduate education or specialised training in motorsport engineering or data analytics. These can deepen your understanding of race car dynamics and sophisticated data analysis techniques.
 5. Trackside Aerodynamicists: The Wind Tamers
5. Trackside Aerodynamicists: The Wind Tamers
Aerodynamics plays a vital role in F1, impacting everything from speed to tyre wear. Trackside Aerodynamicists monitor real-time aerodynamic data during practice sessions and races, comparing it to wind tunnel and Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) data. Their feedback helps adjust the car’s setup for maximum aerodynamic efficiency. The role requires expertise in aerodynamics and CFD, along with proficiency in handling high-tech aerodynamic tools and software.
Career Path to Becoming a Trackside Aerodynamicist
Breaking into the role of a Trackside Aerodynamicist requires a combination of academic credentials, hands-on experience, and a deep understanding of F1 racing. Below is a roadmap that could guide aspiring aerodynamicists:
Pursuing an Appropriate Education:
A degree in Aerospace, Aeronautical or Mechanical Engineering can provide a solid foundation for understanding the principles of aerodynamics. Courses that cover fluid dynamics, thermodynamics, and computational methods can be particularly beneficial.
Specialising in Aerodynamics:
Furthering your education with a master’s degree or specialised courses in aerodynamics can deepen your understanding of this complex field. This can involve studying topics such as wind tunnel testing, Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), and aerodynamic design.
Gaining Practical Experience:
Hands-on experience in aerodynamic testing, whether through internships, education programs, or entry-level jobs, is critical. Working with wind tunnels, CFD simulations, and other aerodynamic testing methods can provide practical insights.
Familiarising with Motorsport Aerodynamics:
Understanding the specifics of aerodynamics in F1 is key. This includes understanding the regulations that govern car design, the role of aerodynamics in car performance, and how different track conditions can affect aerodynamics. There are many technical videos on YouTube that you can learn from, and experts to follow on platforms like Twitter.
Proficiency in Relevant Tools and Software:
Develop proficiency in using CFD software, data analysis tools, and other relevant technologies. The ability to interpret and analyse complex data is vital in this role. Platforms like OpenFOAM are free to use and there are many guides online to help you to get started.
 6. Hospitality: Creating Unforgettable Experiences
6. Hospitality: Creating Unforgettable Experiences
Formula 1 isn’t just about what happens on the track; it’s also about curating memorable experiences off the track. The Hospitality team members are the masterminds behind these experiences, ensuring sponsors, guests, and teams have a smooth and enjoyable F1 experience. The role requires excellent organisational skills, a knack for customer service, and an understanding of how to provide high-quality hospitality under the high-pressure and fast-paced conditions of an F1 race weekend.
Charting Your Career Path in F1 Hospitality
If you’ve got a passion for F1 and love the idea of playing a key role in creating unforgettable experiences, then a career in F1 hospitality could be your calling. Here’s a brief guide on how to set off in this direction:
Start with Hospitality Education:
A degree in hospitality management will provide you with the foundational knowledge and skills you need. These programs often include courses on event management, customer service, food and beverage services, and hospitality law.
Gain Practical Experience:
Get your feet wet by working in the hospitality sector, ideally in a role that involves managing or coordinating events. This will give you practical experience in delivering excellent customer service, handling logistics, and resolving issues that may arise during an event.
Learn about Formula 1:
To work in F1 hospitality, you need to understand the sport and its fans. Attend races, follow the sport closely, and familiarise yourself with the F1 calendar, teams, and drivers.
Apply to F1 Teams:
Once you have some experience and industry connections, start applying to hospitality roles with F1 teams or companies that provide hospitality services at F1 events. A quick internet search will provide a list of companies that provide hospitality services to F1 and other motorsport events.
 7. Physiotherapist: Guardians of Well-being
7. Physiotherapist: Guardians of Well-being
Physiotherapists play an integral role in any Formula 1 team, ensuring drivers are in top shape physically and mentally for the intense demands of racing. They assist drivers in their preparation, recovery, and ongoing conditioning, crafting bespoke exercise and nutritional plans, and providing mental support.
Career Path to Becoming a Physiotherapist for a Formula 1 Team
If you aspire to be a physiotherapist for a Formula 1 team, you’re choosing a career that’s as exciting as it is rewarding. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how you could get there:
Pursuing an Appropriate Education:
You could start by earning a degree in physiotherapy or physical therapy. Some universities offer specific sports physiotherapy programs. This will give you a solid foundation in understanding the human body, movement, and rehabilitation.
Specialising in Sports Physiotherapy:
After gaining your degree, consider a master’s program or further training in sports physiotherapy. This specialty focuses on injury prevention, rehabilitation, and performance enhancement in athletes.
Gaining Practical Experience:
Acquire hands-on experience by working with athletes, ideally in high-intensity sports. This could be at a sports clinic, within a sports club, or as part of a sports event medical team. You’ll learn how to handle common injuries, improve fitness, and boost athletic performance.
Understanding the Demands of F1:
Formula 1 drivers are subject to unique physical and mental pressures. You’ll need to understand the physical demands of driving an F1 car, the common injuries F1 drivers face, and the mental stress associated with the sport.
Building a Network in Motorsport:
As in many professions, networking is key. Attend motorsport events, connect with people in the industry, and build relationships. This can open up opportunities that might otherwise be hard to find.
Joining a Motorsport Team:
With relevant experience and connections, you can seek a position with a motorsport team. You might start with a smaller team and work your way up, or you could work with a driver as their personal physiotherapist.
Together, these roles paint a vivid picture of the diversity and importance of trackside roles. This is only a very small cross-section of the types of trackside roles available in motorsport. Each person’s job, no matter how big or small, contributes to the exhilarating spectacle that is Formula 1 racing. Would you love to work trackside? It’s important to start to prepare yourself early, from the ground up. The competition for positions is fierce and many trackside roles in F1 require you to have built up experience in the factory before moving to a trackside position. How are you ensuring you’ll be the best person for the job?
Quick Heads-Up
We’ve shared some exciting insights on motorsport careers, but remember, your journey is entirely your own! What we’ve suggested are broad strokes – potential paths you could take. The roadmap to success isn’t always so straightforward. We highly recommend that you chat with a career advisor to get personalised advice that suits your aspirations and capabilities. This blog is just a starting point, not a guarantee of career outcomes. After all, every journey has its twists, turns, and pit stops. Happy exploring!
